1. Head off to an interesting destination with your family or friends for an Alternative Identity Day. On the way, everyone makes up his or her own identity. Throughout the day make an effort to play along with that identity: call each other by the chosen faux names, enjoy elaborating on your character’s backstory, and interact with strangers through that identity. At the end of the experiment talk about how it felt to try on an alternative self. And if you’ve taken photos, check to see if anyone held their faces or bodies differently. The sense of observing yourself from the lens of another persona can be illuminating.
2. Start your meal with a toast. It may be as simple as raising your glass of orange juice in the morning, saying “Here’s to a wonderful day ahead.” Or as heartfelt as an unexpected toast to a friend in thanks for all you’ve shared. A toast is a ritual for adding significance to the moment. Why not make more moments significant?
3. Don’t let a day go by without generating some music. You might sing along with the radio or whistle to make a chore go faster. If you play an instrument, even if you haven’t practiced in a long time, get it out (suspending all judgment) and get reacquainted. If you’ve always hankered to play an instrument but never tried, sign up for some introductory lessons.
An easy way to incorporate music into your life is to make up lyrics to familiar tunes. This is particularly satisfying when you’re annoyed. (Whoever passed down the traditional “Rock A Bye Baby” lullaby knew that grumpy lyrics go quite nicely with a sweet tune.) To the tune of “Row, Row, Row, Your Boat” try singing,
Wait, wait, wait on hold Till I want to scream Knowing from experience Service is a dream.See what other experiences you can transform using music.
4. Make an encouraging banner. This project was inspired by the collaborative art project Learning To Love You More. Assignment number 63 was to make an encouraging banner and hang it. Participants hung banners in their bedrooms, across overpasses, in junkyards, alongside roadways, in parking lots—all over the place. In all sorts of colors and shapes their banners announced:
Don’t forget you are beautiful It’s okay to ask for help Life is art Let’s hear it for love Lose track of “I” This is the land of milk & honey You are incomparable Less do, more be You can trust what you can’t explain Farm magicWhat phrase gives you hope? Make a banner, either one you plan to hang in your home or to share with the public. You might want to photograph it in various places. The phrase you love comes alive in different settings.
5. Sketch something you wanted as a child. The perfect treehouse, a fairy godmother, that toy Santa never brought, a first place trophy, a real best friend. Maybe make a few sketches to get the details just the way you want them. Add some labels if that helps. Now close your eyes, imagine yourself as a child, and give this earlier version of yourself that gift. You may scoff but the disappointed child in you just might appreciate the attention.
6. Look for metaphors in the ordinary. Challenge yourself to discern a “message” in the first news item you hear in the day or the first visual that appears when you flick on the TV. Ask yourself why a certain song is playing in your head—does it remind you of something, perhaps a feeling or memory the music evokes? Ask yourself why you might have a certain ache, is your body is speaking to you the only way it can? Look for coincidences, synchronicity, and little delights—these can be signposts indicating you are exactly where you need to be.
In particular, pay attention to the messages found in your dreams. Before going to sleep tell yourself that you will remember your dreams. You may want to ask a question before drifting off. When you wake, don’t jump right out of bed. Instead lie quietly and let dreams rise to your awareness. Although their images and stories often make no logical sense dreams speak in symbols with meaning specific to you. Let those symbols linger with you through the day. Even last night’s giant parking meters demanding soup may start to make sense, metaphorically speaking.
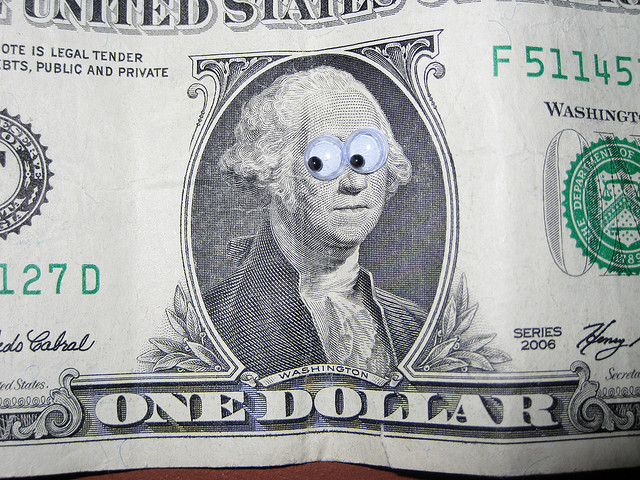
7. Heard of eyebombing? Very simply, it’s the act of putting sticky googly eyes on inanimate objects. As described on eyebombing.com, “Ultimately the goal is to humanize the streets, and bring sunshine to people passing by.”
This is an inexpensive and intentionally silly exercise. Buy a package or two of googly eyes and start looking for where they belong. For inspiration, check out the eyebombing flickr group. Then enjoy your quest. Anthropomorphizing a mustard bottle never seemed so right.